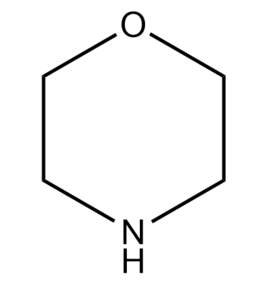
[Physical and chemical properties] Morpholine is also known as morpholine; p-oxoazido has been ring; 1,4-oxoazido hexacyclic. Colorless absorbent oily liquid. Relative density 1.0005, melting point -4.76℃, boiling point 128.3℃, flash point 37.6℃(open cup), vapor pressure 879.9Pa, auto-ignition temperature 310℃, dipole distance 1.58, viscosity 0.00223Pa-s(20℃), surface tension 0.0375N/m(20℃), explosion limit 1.4%~11.20%, refractive index 1.4540(20℃).